Our challenge is to measure the social characteristics of Soldier performance by computing constructs that capture performance such as adaptability, motivational traits, empathy, and commitment to Army Values and the Warrior Ethos. A construct is a composite indicator that measures multi-dimensional concepts (e.g. Warrior Ethos). Constructs are created by developing a conceptual framework useful for identifying and combining data that reflect the dimensions or structure of the characteristics being measured. To create these constructs, we are leveraging existing Department of Defense and external data sources to identify attributes associated with key social behaviors useful for describing Soldier and unit performance.
Developing a Conceptual Performance Framework
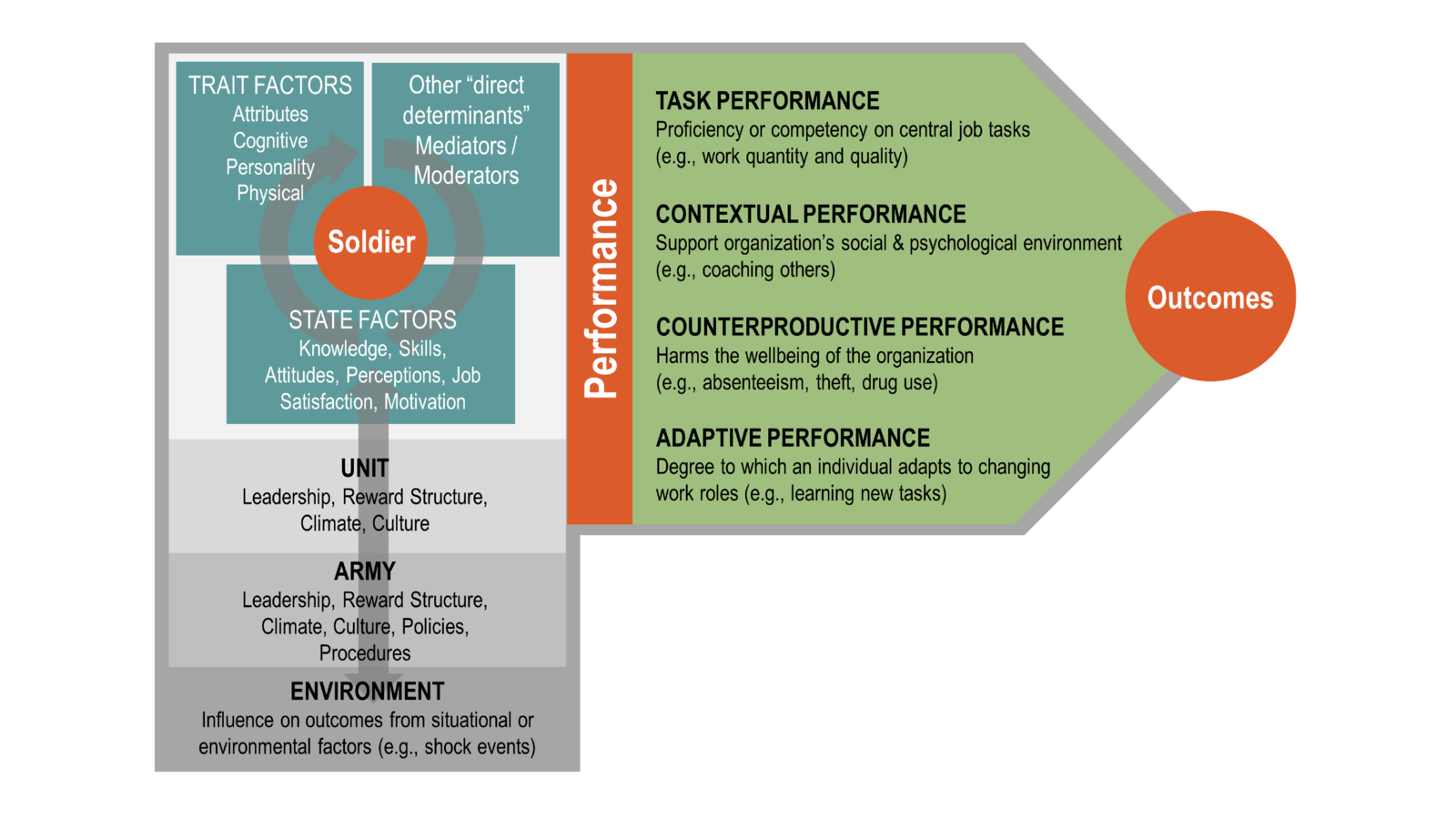
Through the distillation of a vast amount of literature on military and non-military performance we developed a hierarchal performance framework (see Figure 1). It starts with defining a Soldier’s social characteristics by their trait and state factors and direct determinants. Trait factors include attributes, cognitive skills, personality type, and their physical condition. State factors are knowledge, skills, attitudes, perceptions, job satisfaction, and motivation. Direct determinants are mediators and moderators that balance positive and negative behaviors. Next, Soldiers are members of Army units. A unit’s characteristics are influenced by the culture, climate, leadership, and reward structure (i.e., behaviors that are recognized, and valued) within a unit. Units are nested within the overall Army. Army’s characteristics are defined in the same way as a unit but on a larger scale. Finally, external environmental factors that can impact performance outcomes represent shock events, changes in the economy, and other exogenous changes that the Soldier, unit, and Army cannot control.
The conceptual framework maps the different behavioral components of performance as described below.
- Task performance is proficiency or competency on central job tasks.
- Contextual performance supports the organization’s social and psychological environment.
- Counterproductive performance harms the well-being of the organization.
- Adaptive performance is the degree to which an individual adapts to changing work roles.
The intersection of these performance behaviors determines the overall performance along a spectrum of outcomes.
Figures